git@github.swarthmore.edu:CS35-S24/lab08-<your-teamname>CS35: Lab 8: Efficient Keyword Search
Due Wednesday, April 17th at 11:59pm.
Overview
Imagine that you are reading a large PDF document, such as the data structures and algorithms textbook by Shaffer, and you want to find the most relevant pages where priority queues are described. If you search for those keywords in the document, you will most likely be given a sequential list of pages where they occur, rather than a prioritized list, where pages with the most occurrences are first.
In this lab you will write a program that reads in documents, and then repeatedly searches the document for particular keywords. For each search, the program efficiently finds the ten most relevant pages that contain that keyword.
To accomplish this you will build two new implementations of the Dictionary ADT:
-
LinearDictionary -
HashTable
Then you will create a KeywordSearcher class that employs your Dictionary implementations along with an existing implementation of a PriorityQueue to quickly search documents for keywords.
Starting Code
As usual, you can select your partner using Teammaker.
The URL for your repository will be
The following is a description of the repository’s initial comments; bolded files are those which you must change in completing the lab.
-
adts/: As with your last lab, the ADT interface declarations are stored here. The most notable addition for this lab isstlMaxPriorityQueue.h. -
linearDictionary.h/linearDictionary-inl.h: TheLinearDictionaryclass you will be implementing to store collisions within your HashTable. -
hashTable.h/hashTable-inl.h: TheHashTableclass you will be implementing. -
keywordSearcher.h/keywordSearch.cpp: TheKeywordSearcherclass you will be implementing. -
hashFunctions.h/hashFunctions.cpp: The functions used to hash values of different types. -
tests.cpp: The unit testing program you will use to confirm that yourLinearDictionaryandHashTableare correct. -
manualTests.cpp: A sandbox test program for you to use while you develop your program. -
textifyPDF.py: A python program that can be used to convert a PDF document into a text document that is keyword searchable.
Part I. Implementing LinearDictionary
We recommend that you implement a LinearDictionary as a vector of key, value pairs. All of the operations should run in \(O(n)\) time. You may be thinking: "Why would I want such an inefficient implementation of the Dictionary ADT?" The answer is that, for very small dictionaries, simpler implementations perform much better as they have a smaller constant overhead.
We will use the LinearDictionary to represent the chain of collisions in our HashTable. Because we expect each chain to be relatively short, the LinearDictionary provides a nice abstraction that will be efficient enough for our purposes.
Unit tests have been provided for this lab; once you have completed your LinearDictionary implementation, the appropriate unit tests should pass.
Removing from a vector
In order to implement the remove operation of your LinearDictionary, you’ll need to learn about how to remove from a vector.
The vector class provides a means to remove an element from the end of a list (pop_back) but doesn’t give a clear interface for removing elements e.g. from an arbitrary index. Vectors provide a general function called erase which can delete entire contiguous regions:
vector<int> vec = ...;
vec.erase(vec.begin() + start_index, vec.begin() + end_index);The above function works much like a Python slice: the start index is included but the end index is not. Thus, remove_range_from_vector(1,3) would remove the second and third elements (indices 1 and 2) from the vector. If you want to delete a single element from a vector, you can do something like this:
vector<int> vec = ...; // whatever defines this vector
int index = ...; // e.g. 4
vec.erase(vec.begin() + index, vec.begin() + index + 1);Part II. Implementing HashTable
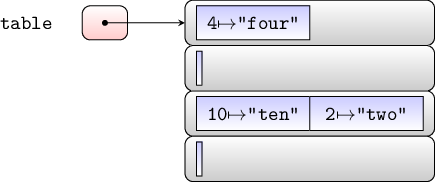
Hash Table Structure
Once your LinearDictionary implementation is complete, you can begin
implementing a chaining hash table as we discussed in class. The
figure at right shows an example of a chaining hash table with size 3,
capacity 4, and storing integer keys with string values.
Here are some important details about this class:
-
We recommend that you use a dynamically allocated array of statically allocated
LinearDictionaryobjects to represent the buckets of yourHashTable. This is not a requirement, but the static allocation of theLinearDictionaryobjects will prevent you from having to allocate and deallocate each bucket yourself. You can also use a dynamically allocated array of dynamically allocatedLinearDictionaryobjects if you prefer. -
One of the constructors allows the user to specify a maximum load factor; the other should use a sensible default value (e.g.
0.75). -
All operations on your
HashTable(other thangetKeysandgetItems) must run in \(O(1)\) average time. -
The
HashTablemust maintain a reasonable load factor in order to operate efficiently. You will likely want to create some private helper methods to assist with increasing the table’s capacity when the load factor becomes too high. (Don’t forget to document those methods according to the Coding Style Requirements below!) -
Note that hashing functions have been provided in
hashFunctions.handhashFunctions.cppfor keys of typeintandstring.
Once you have completed your HashTable implementation, the appropriate unit tests should pass.
Part III. Keyword Searcher
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Document test_data/tiny.txt |
KeywordSearcher |
Once your implementations of the LinearDictionary and HashTable are complete, you can begin implementing the class KeywordSearcher. The figure at right shows an example document that is available in the test_data directory called tiny.txt. Notice that each new page is marked by a special set of characters: $$@@$$PAGE:. You can assume that all documents that you read in will follow this format. The figure also shows a conceptual view of the kind of data structure that your KeywordSearcher should construct. This class will use a hash table keyed on the unique words within a document. Associated with each word is another structure that tracks the page numbers where that word occurs and the number of times it appears on that page.
Here are some important details about this class:
-
You have the opportunity to design the underlying data structure within this class. At the topmost level you must use a
HashTablekeyed on the unique words within the document, but you may choose the value associated with these keys. Here are two suggestions:-
Use a dynamically allocated
HashTablekeyed on page numbers and storing the number of occurrences on that page. -
Use an instance of a new class that you create. This class could provide a nice layer of abstraction for more clearly accessing the information we care about for this application.
-
-
Whatever data structure you choose, your implementation must find all pages where a word occurs in a document in \(O(1)\) average time.
-
Again, we encourage you to write any private helper methods that you need to assist with completing the required public methods for this class:
loadWordsandsearch. -
To determine the top ten most relevant pages, you will use the
STLMaxPriorityQueueclass (see its interface in theadtsdirectory). Notice that one of its constructors takes avector<pair<P, V>>as an argument and will heapify it. By using the number of occurrences of a word as the priority, and the page number as the value, you can use the resulting priority queue to efficiently find the top ten most relevant pages by repeatedly removing the maximum from it. Note that use of a priority queue is required; your top ten algorithm must run in \(O(m)\) time, where \(m\) is the number of matching pages. You can’t simply sort the matching pages; this would take \(O(m \log m)\) time.
Once you have completed your KeywordSearcher implementation, the appropriate unit tests should pass.
Part IV. Main Program
The final part of your lab is to implement the main program, which will read in a document as a text file, and allow the user to repeatedly search the document for particular keywords. If the text file does not exist, your program should end gracefully:
./keywordSearch foo
Unable to open file fooFor each keyword search, it returns the top ten pages within the document that contain that keyword the most times. If the word doesn’t appear on at least ten pages, then it should return as many pages as it can. It should also gracefully handle the case where the word does not appear at all within the document.
For instance, here is a sample run of the program done on the contents of the data structures textbook stored in the test_data subdirectory:
./keywordSearch test_data/DataStructuresAndAlgorithmAnalysis.txt
File loaded
Please enter a search word or '!' to quit: priority
The word priority appears in the file...
on page 220 (11 occurrences)
on page 197 (8 occurrences)
on page 204 (7 occurrences)
on page 206 (5 occurrences)
on page 421 (5 occurrences)
on page 612 (3 occurrences)
on page 422 (2 occurrences)
on page 203 (2 occurrences)
on page 425 (2 occurrences)
on page 543 (2 occurrences)
Please enter a search word or '!' to quit: queue
The word queue appears in the file...
on page 150 (23 occurrences)
on page 148 (22 occurrences)
on page 149 (12 occurrences)
on page 152 (9 occurrences)
on page 153 (8 occurrences)
on page 151 (8 occurrences)
on page 417 (7 occurrences)
on page 147 (7 occurrences)
on page 166 (5 occurrences)
on page 220 (5 occurrences)
Please enter a search word or '!' to quit: swarthmore
The word swarthmore does not appear in the file.
Please enter a search word or '!' to quit: !
Goodbye!Memory
For this lab, your program is required to run without memory errors or leaks. You should use valgrind as you proceed in your testing to track memory errors. When you have a complete first draft of your implementation:
-
Commit and push what you have (in case something goes wrong).
-
Run
valgrind ./teststo make sure that the test program does not cause memory errors. -
Once memory errors are cleared, run
valgrind --leak-check=full ./teststo identify and correct memory leaks. -
Note:
valgrindmay take several minutes to run on the unit tests for this lab.
Coding Style Requirements
As usual, you will also be required to observe good coding practices:
-
For each class, document all data members and methods in the .h files.
-
Your C++ code must have proper and consistent indentations.
-
You must have proper and consistent usage of spacing and braces for
if,else,for, andwhileconditions as well as class definitions and code blocks.
Summary of Requirements
When you are finished, you should have
-
A completed implementation of
LinearDictionary -
A completed implementation of
HashTable -
A completed implementation of
KeywordSearcher -
A completed
mainprogram that ensures the proper number of command-line arguments and handles bad filenames gracefully -
No memory errors
-
No memory leaks
-
Code which conforms to the style requirements